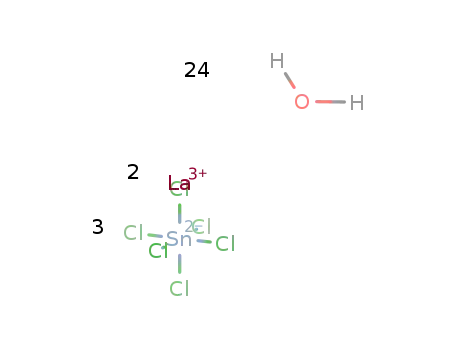
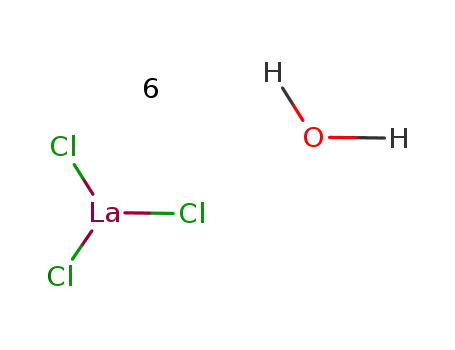
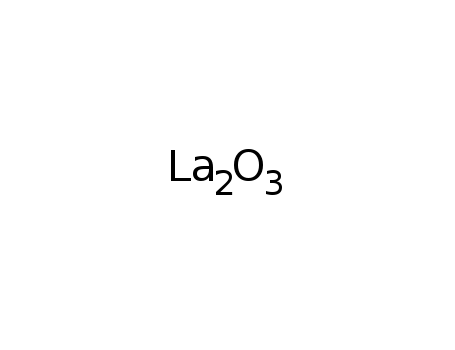Reduced lanthanum halides with Ge as interstitials: La2I 2Ge, La2I2Ge2, La3Cl 2Ge3, La3Br2Ge3, La 3I3Ge, La
Mattausch, Hansjuergen,Zheng, Chong,Ryazanov, Mikhail,Simon, Arndt
, p. 302 - 308 (2005)
The title compounds were synthesized fro...
1D-Polyoxometalate-Based Composite Compounds - Design, Synthesis, Crystal Structures, and Properties of [{Ln(NMP)6}(PMo12O 40)]n (Ln = La, Ce, Pr; NMP = N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone)
Niu, Jing-Yang,Wei, Mei-Lin,Wang, Jing-Ping,Dang, Dong-Bin
, p. 160 - 170 (2004)
The structures of three 1:1 composite co...
Gelation of La(III) cations promoted by 5-(2-pyridyl)tetrazolate and water
Andrews, Philip C.,Junk, Peter C.,Massi, Massimiliano,Silberstein, Morry
, p. 3317 - 3319 (2006)
Addition of water to the product formed ...
Synthesis and structure of the new compound La2O(CN 2)2 possessing an interchanged anion proportion compared to the parent La2O2(CN2)
Srinivasan, Radhakrishnan,Tragl, Sonja,Meyer, H.-Juergen
, p. 719 - 722 (2005)
La2O(CN2)2 was synthesized from a 1:1:2 ...
Catalytic hydrogen-chlorine exchange between chlorinated hydrocarbons under oxygen-free conditions
Van Der Heijden, Alwies W. A. M.,Podkolzin, Simon G.,Jones, Mark E.,Bitter, Johannes H.,Weckhuysen, Bert M.
, p. 5002 - 5004 (2008)
(Figure Presented) Pass the parcel: Acti...
Destabilization of LiBH4 by (Ce, La)(Cl, F)3 for hydrogen storage
Zhang, Bang Jie,Liu, Bin Hong,Li, Zhou Peng
, p. 751 - 757 (2011)
The mixtures of LiBH4 with halides of Ce...
Study of the chemical chelates and anti-microbial effect of some metal ions in nanostructural form on the efficiency of antibiotic therapy norfloxacin drug
Refat, Moamen S.,El-Hawary,Mohamed, Mahmoud A.
, p. 45 - 54 (2012)
This paper has reviewed the chemical and...
Rare earth halides Ln4X5Z. Part 3: The chloride La4Cl5B4 - Preparation, structure, and relation to La4Br5B4, La4I5B 4
Mattausch, Hansjuergen,Oeckler, Oliver,Simon, Arndt
, p. 503 - 506 (2008)
La4Cl5B4 is synthesized by reaction of L...
Lanthanum phosphite microspheres: Hydrothermal synthesis, ab initio structure determination, morphology and photoluminescence of La(HO)(HPO 3)
Xiong, Ding-Bang,Zhao, Yu-Feng,Gulay, Lubomir D.,Zhao, Jing-Tai
, p. 4522 - 4527 (2009)
Lanthanum phosphite microspheres with di...
Lanthanum(III) chloride complexes with heterocyclic Schiff bases : SSynthesis, spectroscopic characterization and thermal studies
Thankamony,Sindhu Kumari,Mohanan,Rijulal
, p. 259 - 266 (2009)
Condensation of 2-amino-3-carboxyethyl-4...
Luminescence and structural properties of lanthanide complexes of Schiff bases derived from pyridoxal and amino acids
Puntus, Lada,Zhuravlev, Konstantin,Lyssenko, Konstantin,Antipin, Mikhail,Pekareva, Irina
, p. 4079 - 4088 (2007)
Lanthanide complexes of Schiff bases (SB...
Kinetics and mechanism of the thermal decomposition of lanthanum complexes of 4-N-(4'-antipyrylmethylidene) aminoantipyrine
Nair, M. K. Muraleedharan,Radhakrishnan, P. K.
, p. 141 - 150 (1995)
The kinetics and mechanism of the therma...
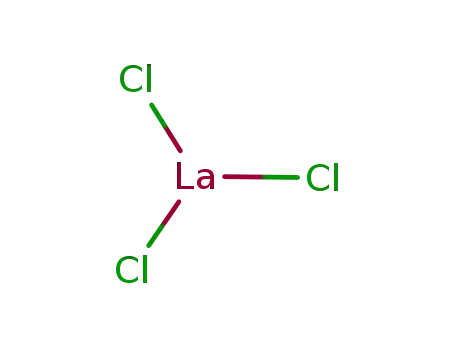
Bridgman growth of LaCl3:Ce3+ crystal in non-vacuum atmosphere
Chen, Hongbing,Yang, Peizhi,Zhou, Changyong,Jiang, Chengyong
, p. 172 - 175 (2008)
Growth of LaCl3:Ce3+ crystal by the vert...
Thermal decomposition kinetics of lanthanum complexes of 1,2-(diimino-4′-antipyrinyl)ethane
Nair,Radhakrishnan
, p. 475 - 480 (1998)
The kinetics and mechanism of the therma...
Layered lanthanum carbide halide superconductors La2C2(X,X′)2 (X,X′ = Cl, Br, I): Neutron powder diffraction characterization and electronic properties
Ahn, Kyungsoo,Gibson, Brendan J.,Kremer, Reinhard K.,Mattausch, Hansjuergen,Stolovits, Andres,Simon, Arndt
, p. 5446 - 5453 (1999)
The superconducting properties of La2C2(...
Molecular nitrides with titanium and rare-earth metals
Caballo, Jorge,Garcia-Castro, Maria,Martin, Avelino,Mena, Miguel,Perez-Redondo, Adrian,Yelamos, Carlos
, p. 6798 - 6808 (2011)
A series of titanium-group 3/lanthanide ...
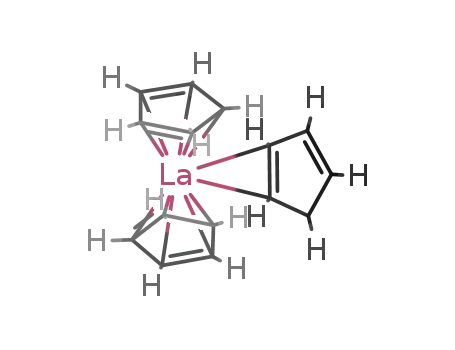
Synthesis, characterization, and reactivity of ansα-Bis(allyl) Lanthanide complexes, a new class of single-component methyl methacrylate polymerization catalysts
Woodman, Timothy J.,Schormann, Mark,Bochmann, Manfred
, p. 2938 - 2943 (2003)
The reaction of the dipotassium salt K2{...
Description and Structure of New Compounds Ln//3MO//5XCl//3 (Ln EQUVLNT La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Th; M EQUVLNT Ta, Nb; X EQUVLNT O, OH, F).
Schaffrath, U.,Gruehn, R.
, p. 61 - 74 (1988)
La//2ThTaO//6Cl//3, a representative of ...
A cluster with a mixed M6X12/M6X8 environment: The La6Cl11Co structure
Zheng, Chong,Mattausch, Hansjuergen,Hoch, Constantin,Simon, Arndt
, p. 2307 - 2311 (2009)
The title compound was synthesized from ...
Chlorination of lanthanum oxide
Gaviria, Juan P.,Navarro, Lucas G.,Bohe, Ana E.
, p. 2062 - 2070 (2012)
The reactive system La2O3(s)-Cl2(g) was ...
MOF formation vs. reversible high ligand uptake in anhydrous halides: Two opposing aspects of ∞3 [La2CI6(4,4'-bipy) 5]·4(4,4'-bipy)
Hoeller, Christoph J.,Matthes, Philipp,Beckmann, Jens,Mueller-Buschbaum, Klaus
, p. 395 - 399 (2010)
Construction of the framework, structure...
Microstructure and desorption properties study of catalyzed NaAlH 4
Xueping, Zheng,Xin, Feng,Shenglin, Liu
, p. 5873 - 5876 (2011)
NaAlH4 catalyzed by Ce(SO4)2 and LaCl 3 ...
Electrodeposition of RE-TM (RE = La, Sm, Gd; TM = Fe, Co, Ni) films and magnetic properties in urea melt
Li, Jiaxin,Lai, Heng,Fan, Biqiang,Zhuang, Bin,Guan, Lunhui,Huang, Zhigao
, p. 547 - 551 (2009)
Rare earth (RE)-3d transition metal (TM)...
Electro-deposition of Co-La alloy films in urea melt and their performances
Wang, Sen-Lin,Lin, Ji-Bei,Cai, Qiu-Yan,Zhang, Yan
, p. 142 - 147 (2008)
The Co-La alloy film was electro-deposit...
Two structurally related oxide nitride chalcogenides of the lanthanoids: Tb3ONSe2 and la5O2NS4
Lissner, Falk,Strobel, Sabine,Schleid, Thomas
, p. 149 - 156 (2010)
The structurally related oxide nitride c...
La3Cl3BC - Structure, bonding and electrical conductivity
Zeng, Hui-Yi,Okudera, Hiroki,Zheng, Chong,Mattausch, Hansjürgen,Kremer, Reinhard K.,Simon, Arndt
, p. 499 - 504 (2005)
A new rare earth carbide boride halide, ...
Spectrum analysis, correlation crystal-field effects and f-f transition intensities of U3+ in LaCl3
Karbowiak,Drozdzynski,Sobczyk
, p. 2800 - 2800 (2002)
-
Zintl anions of silicon in the halides La3Cl2Si3 and La6Br3Si7
Mattausch, Hansjuergen,Oeckler, Oliver,Simon, Arndt
, p. 297 - 301 (1999)
La3Cl2Si3 and La6Br3Si7 are prepared at ...
Local structure of molten LaCl3 analyzed by X-ray diffraction and La-LIII absorption-edge XAFS technique
Iwadate,Suzuki,Onda,Fukushima,Watanabe,Matsuura,Kajinami,Takase,Ohtori,Umesaki,Kofuji,Myochin
, p. 248 - 252 (2006)
From the radial distribution analysis of...
High-temperature infrared spectroscopy of YCl3: the vibration spectrum, molecular structure and thermodynamic functions
Konings, R. J. M.,Booij, A. S.
, p. 183 - 190 (1992)
The infrared spectrum of gaseous YCl3 ha...
Sheets of La6(C2) octahedra in lanthanum carbide chlorides - Undulated and plane
Mattausch, Hansjuergen,Simon, Arndt,Kienle, Lorenz,Koehler, Juergen,Hoch, Constantin,Nuss, Juergen
, p. 2765 - 2776 (2008)
The reaction of Ln, LnCl3 (Ln = La, Ce) ...
Pulse current electrodeposition of Al from an AlCl3-EMIC ionic liquid
Li, Bing,Fan, Chunhua,Chen, Yan,Lou, Jingwei,Yan, Lingguang
, p. 5478 - 5482 (2011)
Electrodeposition of aluminum from an Al...
INTERNAL ROTATION AND PHASE TRANSITIONS IN LANTHANUM TETRAHYDROBORATES
Volkov, V. V.,Khikmatov, M.,Mirsaidov, U.,Gabuda, S. P.,Kozlova, S. G.
, p. 58 - 61 (1988)
Usig the 1H, 11B, 139La NMR and relaxati...
Luminescent properties of ytterbium-doped ternary lanthanum chloride
Kaminska,Cybińska,Zhydachevskii,Sybilski,Meyer,Suchocki
, p. 7993 - 7997 (2011)
Studies of the absorption and temperatur...
Thermal and spectroscopic studies on solid Ketoprofen of lighter trivalent lanthanides
Galico, D. A.,Holanda, B. B.,Perpetuo, G. L.,Schnitzler, E.,Treu-Filho, O.,Bannach, G.
, p. 371 - 380 (2012/04/23)
Solid-state Ln(L)3 compounds, where Ln s...
Synthesis, thermal properties and spectroscopic study of solid mandelate of light trivalent lanthanides
Gigante,Gomes,Lima,Caires,Treu-Filho,Ionashiro
, p. 6 - 14 (2012/05/31)
Characterization, thermal stability and ...